The Intrinsic and Extrinsic Clot Pathway
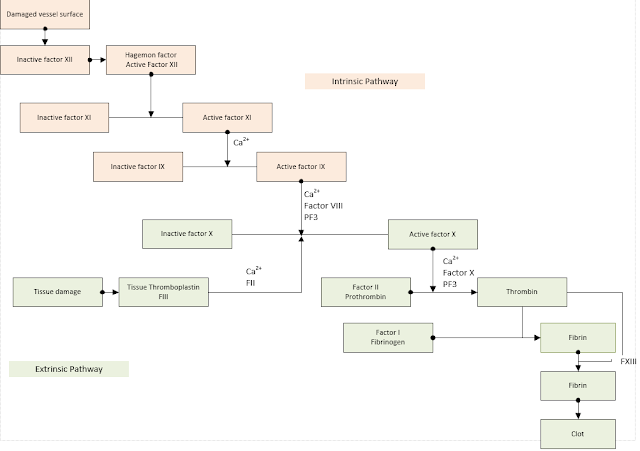
When damage occurs to tissues, or there is damage to a nerve, a number of vascular responses occur.
Neutrophils are attracted to the injured site which stimulates the release of histamine, basophils, platelets, mast cells, and kinins.
Prostaglandins and lipids are released from the damaged cells. Vasodilation and increased permeability of blood vessels cause heat, redness, and swelling. Pain occurs from damage to the nerves, as well as toxic chemicals which are released from microbes. Kinins can irritate nerve endings while prostaglandins intensify and prolong the pain.

Comments
Post a Comment